Light and Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants absorb light energy, assimilate carbon dioxide and water, produce organic matter and release oxygen. Photosynthesis produces mainly sugars and stores energy. Light energy is the energy source of photosynthesis in plants, but plants absorb different amounts of light at different wavelengths, and their photosynthetic products are different. Studies have shown that under the irradiation of red light, leaves form a large amount of carbohydrate, with less protein. When the blue light is irradiated, the carbohydrate decreases while the protein content increases.
Light saturation phenomenon and light compensation point. Photosynthesis is a photobiochemical reaction. Within a certain range, the photosynthetic rate increases with the increase of light intensity, but beyond a certain range, when the light reaches a certain intensity, the photosynthetic rate does not increase. This phenomenon is called light saturation. The light saturation point of the heliophytes is higher than that of the heliophytes. Because when the group leaves are flourishing, the external light is very strong, reaching above the light saturation point of single leaf, while the light intensity inside the group is still below the light saturation point, the middle and lower leaf leaves make full use of the transmission light and reflected light, the group light rate will rise.
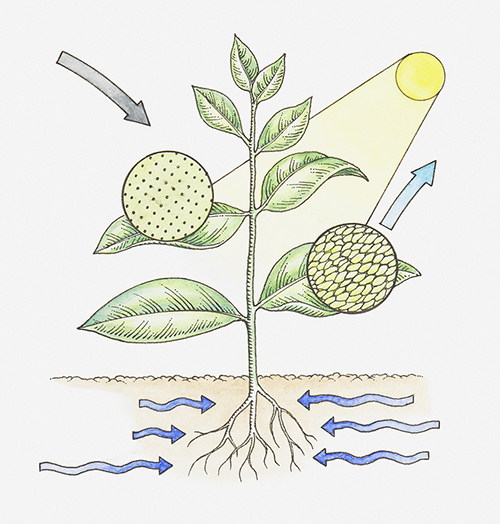
In addition, as the light decreases, the rate of photosynthesis gradually approaches the rate of respiration, reaching a point at which photosynthesis equals the rate of respiration. In the same leaf at the same time, the CO2 absorbed by the photosynthetic process and CO2 released by the respiration process is equivalent in an intensity of light, which is called the light compensation point. At this point, the photosynthetic accumulation and absorption of organic matter equal, the plant do not grow. Therefore, in order to ensure the normal growth of crops, the light intensity must be greater than the light compensation point. So how do you make the light more intense than the compensation point?
(1) Extended Photosynthetic Time
Lengthening photosynthetic time is to maximize the use of light time and improve the utilization rate of light energy. The specific measures are as follows:
1. Increase the multiple seed index. It means to increase the ratio of the harvested area of crops to the cultivated area in the whole year. Specific practice is the four seasons rotation, reasonable interplanting. In one year, various crops are skillfully matched, so as to make better use of light energy in time and space, shorten the idle time of fields and reduce the rate of light leakage.
2. Extend the growth period. On the premise of not affecting the farming system, the crop growth period should be extended appropriately.
3. Supplement of artificial light. Under the cultivation of small area, when the sunlight is insufficient or the sunlight time is too short, it can be supplemented by artificial light. LED growing lights are the ideal artificial light source, and the spectral composition is similar to that of sunlight.
For LED grow lights, you can check out this fellow article:
《Why Does The LED Grow Lights Need to Dissipate Heat?》
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants absorb light energy, assimilate carbon dioxide and water, produce organic matter and release oxygen. Photosynthesis produces mainly sugars and stores energy. Light energy is the energy source of photosynthesis in plants, but plants absorb different amounts of light at different wavelengths, and their photosynthetic products are different. Studies have shown that under the irradiation of red light, leaves form a large amount of carbohydrate, with less protein. When the blue light is irradiated, the carbohydrate decreases while the protein content increases.
Light saturation phenomenon and light compensation point. Photosynthesis is a photobiochemical reaction. Within a certain range, the photosynthetic rate increases with the increase of light intensity, but beyond a certain range, when the light reaches a certain intensity, the photosynthetic rate does not increase. This phenomenon is called light saturation. The light saturation point of the heliophytes is higher than that of the heliophytes. Because when the group leaves are flourishing, the external light is very strong, reaching above the light saturation point of single leaf, while the light intensity inside the group is still below the light saturation point, the middle and lower leaf leaves make full use of the transmission light and reflected light, the group light rate will rise.

In addition, as the light decreases, the rate of photosynthesis gradually approaches the rate of respiration, reaching a point at which photosynthesis equals the rate of respiration. In the same leaf at the same time, the CO2 absorbed by the photosynthetic process and CO2 released by the respiration process is equivalent in an intensity of light, which is called the light compensation point. At this point, the photosynthetic accumulation and absorption of organic matter equal, the plant do not grow. Therefore, in order to ensure the normal growth of crops, the light intensity must be greater than the light compensation point. So how do you make the light more intense than the compensation point?
(1) Extended Photosynthetic Time
Lengthening photosynthetic time is to maximize the use of light time and improve the utilization rate of light energy. The specific measures are as follows:
1. Increase the multiple seed index. It means to increase the ratio of the harvested area of crops to the cultivated area in the whole year. Specific practice is the four seasons rotation, reasonable interplanting. In one year, various crops are skillfully matched, so as to make better use of light energy in time and space, shorten the idle time of fields and reduce the rate of light leakage.
2. Extend the growth period. On the premise of not affecting the farming system, the crop growth period should be extended appropriately.
3. Supplement of artificial light. Under the cultivation of small area, when the sunlight is insufficient or the sunlight time is too short, it can be supplemented by artificial light. LED growing lights are the ideal artificial light source, and the spectral composition is similar to that of sunlight.
For LED grow lights, you can check out this fellow article:
《Why Does The LED Grow Lights Need to Dissipate Heat?》
《The FAQ of LED Grow Lights》
(2) Increase Photosynthetic Area:The photosynthetic area is the green area of plants, mainly leaf area, which has the greatest impact on yield and is also an easy to control aspect.
1. Reasonably close planting. It mainly deals with the relationship between the group and the individual, the species is too sparse, the individual develops well, but the group is not fully developed, and the light energy utilization rate is low. If planted too tightly, the lower leaf receives less light and becomes a consuming organ below the light compensation point, the photosynthetic productivity will decrease and it will also decrease.
2. Change the plant type. High yield cultivars of good plant type were selected, that is, short stem, straight and thick leaf, dense tillering. In other words, it can increase the density of planting, increase the photosynthetic area, resist fertilizer, make full use of light energy and improve the utilization rate of light energy.
Improve photosynthetic efficiency. Good ventilation in the field, ensuring the supply of CO2, or increasing the concentration of CO2 in the field can improve the photosynthetic efficiency per unit area. At present, the commonly used method is, the first is to adjust to local conditions, to ensure ventilation. Second, organic farm manure and ammonium bicarbonate fertilizer were added, which not only increased nitrogen but also increased CO2 concentration in the field. The third is to use photorespiration inhibitors to inhibit photorespiration and improve light and ability.
The Relationship Between Light and Plant Growth
Generally speaking, the growth and development of plants are carried out under sunlight. Different spectra have different effects on many kinds of light reaction phenomena, such as photosynthesis, growth, development, a formation of chlorophyll, phototropism, and induction of photomorphogenesis.
(1)The effect of light on the growth of vegetative organs.
The seedling development is controlled by light. Seeds of cereal crops, sheaths and mesocotyls sown in the soil elongate until the light is seen. When the seedlings see light, the curly leaves open. Light inhibits stem elongation. Light also inhibits root growth of various crops, and the intensity of light is positively correlated with root growth inhibition.
(2) Phototropism of plant growth.
The ability of a plant to bend in the direction of light is called phototropism. If the leaves can be extended as far as possible in the best use of light energy position. The reason for the phototropism is that the light from one side can cause the auxin to be transported laterally to the backlight side, thus making the auxin on the back side more and the cell elongation is intense, so the plant grows to the light and bends. In addition, the study found that it was a short-wavelength light that played a role in the direction of light, while the red light was ineffective.
(3)The effects of sunlight on flowering and dormancy of plants
1. Effect of sunshine length on plant flowering. Plant flowering has photoperiod, and the length of sunlight has a decisive influence on the length of time from vegetative growth to flower stem formation. Studies have shown that the photoperiod of plant flowering, during the photoperiod and dark period, is the dark period. That is, short sunlight plants must exceed a critical dark period to form flower buds; Plants with long sunshine must be shorter than a critical dark period before they can bloom. The flash test proves the importance of the dark period.
2. Effects of light on plant dormancy. Many studies show that autumn leaves and winter dormancy of temperate plants are related to the length of sunshine. Short sunlight can push the plants into hibernation. For example, poplar trees, after being given a few days of short sunshine, will form a terminal bud even if the temperature is still quite high. If the short sunshine treatment continues (the temperature condition remains unchanged), the leaves will no longer grow, then gradually fade off and enter deep dormancy. If treated with long sunshine again, the plant can continue to grow without going into hibernation. Tree species such as acacia and poplar also reacted to the short sunshine. Therefore, in the introduction work of the northern botanical garden, short sunlight can be used to induce early dormancy of trees and enhance the ability to resist cold and winter.

(4)Light plays a certain role in inducing morphological formation, phototropism, and pigment formation.
For example, the blue-violet and blue-green light in visible light can inhibit the elongation of plants, thus causing plants to form short forms. Blue, blue and violet light can cause the sensitivity of plant phototropism and promote the formation of anthocyanins and other plant pigments. Blue light can activate the enzymes that assimilate CO2 in photosynthesis. Ultraviolet light can inhibit the growth factor formation and stem elongation. Alpine plants stem dwarf, leaf surface shrinking, stem leaves rich in anthocyanin, and so on, and high mountain blue, purple, green, such as shortwave light and more ultraviolet light.
In recent years, the application of colored films in agriculture has been more and more extensive. For example, compared with the natural color film, the seedling and root system of the light blue film are stronger, the seedling and root system of the former are quick to survive, the tillering is early and many, and the content of various nutrients of rice is higher.

Therefore, the correct understanding of the relationship between light and plants is more conducive to the improvement of crop quality and yield.
(2) Increase Photosynthetic Area:The photosynthetic area is the green area of plants, mainly leaf area, which has the greatest impact on yield and is also an easy to control aspect.
1. Reasonably close planting. It mainly deals with the relationship between the group and the individual, the species is too sparse, the individual develops well, but the group is not fully developed, and the light energy utilization rate is low. If planted too tightly, the lower leaf receives less light and becomes a consuming organ below the light compensation point, the photosynthetic productivity will decrease and it will also decrease.
2. Change the plant type. High yield cultivars of good plant type were selected, that is, short stem, straight and thick leaf, dense tillering. In other words, it can increase the density of planting, increase the photosynthetic area, resist fertilizer, make full use of light energy and improve the utilization rate of light energy.
Improve photosynthetic efficiency. Good ventilation in the field, ensuring the supply of CO2, or increasing the concentration of CO2 in the field can improve the photosynthetic efficiency per unit area. At present, the commonly used method is, the first is to adjust to local conditions, to ensure ventilation. Second, organic farm manure and ammonium bicarbonate fertilizer were added, which not only increased nitrogen but also increased CO2 concentration in the field. The third is to use photorespiration inhibitors to inhibit photorespiration and improve light and ability.
The Relationship Between Light and Plant Growth
Generally speaking, the growth and development of plants are carried out under sunlight. Different spectra have different effects on many kinds of light reaction phenomena, such as photosynthesis, growth, development, a formation of chlorophyll, phototropism, and induction of photomorphogenesis.
(1)The effect of light on the growth of vegetative organs.
The seedling development is controlled by light. Seeds of cereal crops, sheaths and mesocotyls sown in the soil elongate until the light is seen. When the seedlings see light, the curly leaves open. Light inhibits stem elongation. Light also inhibits root growth of various crops, and the intensity of light is positively correlated with root growth inhibition.
(2) Phototropism of plant growth.
The ability of a plant to bend in the direction of light is called phototropism. If the leaves can be extended as far as possible in the best use of light energy position. The reason for the phototropism is that the light from one side can cause the auxin to be transported laterally to the backlight side, thus making the auxin on the back side more and the cell elongation is intense, so the plant grows to the light and bends. In addition, the study found that it was a short-wavelength light that played a role in the direction of light, while the red light was ineffective.
(3)The effects of sunlight on flowering and dormancy of plants
1. Effect of sunshine length on plant flowering. Plant flowering has photoperiod, and the length of sunlight has a decisive influence on the length of time from vegetative growth to flower stem formation. Studies have shown that the photoperiod of plant flowering, during the photoperiod and dark period, is the dark period. That is, short sunlight plants must exceed a critical dark period to form flower buds; Plants with long sunshine must be shorter than a critical dark period before they can bloom. The flash test proves the importance of the dark period.
2. Effects of light on plant dormancy. Many studies show that autumn leaves and winter dormancy of temperate plants are related to the length of sunshine. Short sunlight can push the plants into hibernation. For example, poplar trees, after being given a few days of short sunshine, will form a terminal bud even if the temperature is still quite high. If the short sunshine treatment continues (the temperature condition remains unchanged), the leaves will no longer grow, then gradually fade off and enter deep dormancy. If treated with long sunshine again, the plant can continue to grow without going into hibernation. Tree species such as acacia and poplar also reacted to the short sunshine. Therefore, in the introduction work of the northern botanical garden, short sunlight can be used to induce early dormancy of trees and enhance the ability to resist cold and winter.

(4)Light plays a certain role in inducing morphological formation, phototropism, and pigment formation.
For example, the blue-violet and blue-green light in visible light can inhibit the elongation of plants, thus causing plants to form short forms. Blue, blue and violet light can cause the sensitivity of plant phototropism and promote the formation of anthocyanins and other plant pigments. Blue light can activate the enzymes that assimilate CO2 in photosynthesis. Ultraviolet light can inhibit the growth factor formation and stem elongation. Alpine plants stem dwarf, leaf surface shrinking, stem leaves rich in anthocyanin, and so on, and high mountain blue, purple, green, such as shortwave light and more ultraviolet light.
In recent years, the application of colored films in agriculture has been more and more extensive. For example, compared with the natural color film, the seedling and root system of the light blue film are stronger, the seedling and root system of the former are quick to survive, the tillering is early and many, and the content of various nutrients of rice is higher.

Therefore, the correct understanding of the relationship between light and plants is more conducive to the improvement of crop quality and yield.
没有评论:
发表评论